Introduction to Dog Anxiety
Dogs sometimes suffer from a silent but intolerable problem called dog anxiety. This widespread mental health disorder that comes with droopy ears and fur can actually affect their health, leading to behavioral problems. Other influences such as changes in nature, climate, and family can help in the development of anxiety in dogs. Identifying the symptoms and knowing the causes that affect our pets should be the first step towards helping our pets in pain.
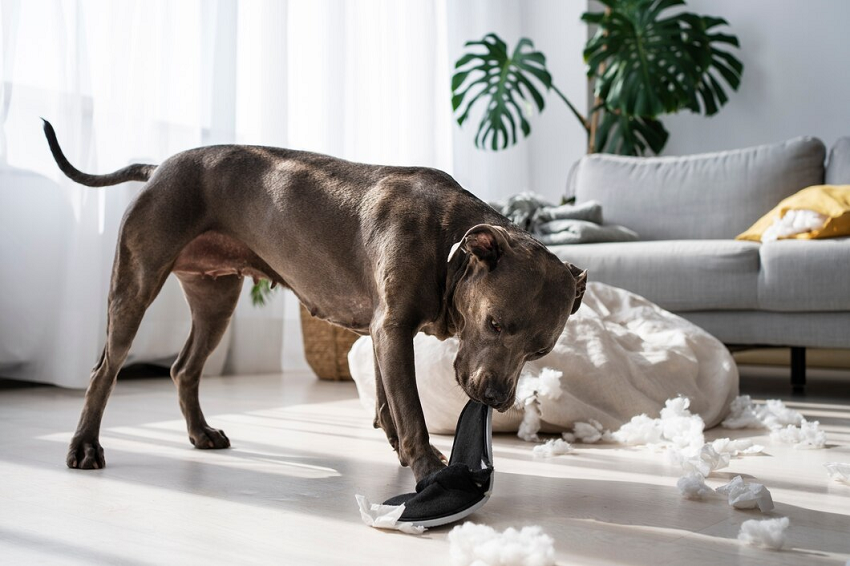

Establishing the root causes of dog anxiety is very useful in trying to solve the problem. There remain some interrelationships between genetics and past events, ecology, and physiology. Other reactions that are associated with previous or unaddressed socialization would include separation anxiety.
Fear of noise is a problem affecting many dogs, in which they are prone to overreacting to certain sounds such as loud noises that come with thunder or firecrackers. Other environmental factors such as places, people, or other animals that the dog has never seen before or other factors can also cause the dog to experience anxiety. In such cases, you need to understand why your dog is experiencing anxiety and how to treat this problem.
Let’s understand what causes dog anxiety, common symptoms, and possible treatments in detail. It is essential to have a good friendship with your pet buddy.
What is Dog Anxiety?
Dog anxiety means a state of concern or shakiness that occurs because of some trigger or a specific disease. It varies from simple discomfort to greatly distressed, including anxiety attacks. However, fear and stress sometimes are innate for dogs, and when dogs suffer from a strong, persistent anxiety that strongly affects their lives, this needs medical assistance.
Causes of Dog Anxiety
There is a broad range of sources of dog anxiety and they can be caused by numerous conditions, from environmental ones to health problems. When pet owners recognize these causes, they can effectively manage their dog’s anxiety and create the best treatment program. Some common causes of dog anxiety include:
Trauma and Past Experiences
Anxiety can come from fear factors and puppies that were not socialized young may be afraid of something that is in their environment. Dogs encounter such cases which lead to developing an added amount of fear and anxiety in the dogs and thus a difficult situation for dogs to adapt to different situations or places.
Separation Anxiety
One form of behavioral problem the commonly affects dogs especially those that are closely bonded with their owners is separation anxiety. Dogs going through this condition will show destructive behavior after being left alone, excessive barking and more.
Changes in Environment
Just as any other dog, stress is also experienced by pets’ toy-poodles due to changes that may involve moving from one house to the other or when pets are taken to live with new animals in that house. These changes can create anxiety in the dog and thus lead to increased stress and exhibit of other behavioral problems.
Fear of Specific Stimuli
There are specific causes that can provoke anxiety for dogs – noise, strangers, or other animals for example. These fears cause anxiety and can result in practices such as avoiding being excessively loud – barking or exhibiting other signs of anxiety.
Health Issues
Medical conditions, including hypothyroidism or possible brain disorders, can cause the dog to become unbalanced. These health problems can bring about physical signs that may be mistaken for anxiety hence the need for a dog owner to seek veterinary advice when they think that their pet is anxious due to a health complication.
Symptoms of Dog Anxiety
Such anxieties may be concealed at first, but more apparent in dogs as time passes in a day or in a week. Some common symptoms of dog anxiety include:
Behavioral Changes
The most typical sign of dog anxiety is when behavior is modified and easily observable. Some of the behavioral changes associated with dog anxiety include:
- Excessive barking or whining: An anxious dog will constantly bark or whine as a way of letting their owner know that they are not comfortable. If the source of the anxiety is chronic, the dog may find the escape from these vocalizations extremely difficult.
- Restlessness or pacing: A dog who is anxious will not know how to relax or lay down. They could walk over the place feeling they cannot settle down, or they would make round after round to run away from the anxiety that grips them.
- Aggression: An anxious dog sometimes becomes aggressive and brings harm to the properties of individuals or other pets. Such behavior is not safe and should be handled by a professional.
- Destructive behaviors: Any canine that has anxiety will focus its destructive feelings on objects including furniture, cushions, or flowers in the compound.
Physical Signs
But behavioral changes in dogs are only one sign of anxiety, there can be other signs in dogs as well as physical problems. Some of the most common physical symptoms include:
- Trembling or shaking: Some dogs will shake or tremble, because their body becomes stiff and alert when they are anxious. This may be accompanied by other symptoms or signs such as labored breathing or widened pupils.
- Panting or drooling excessively: Whether it is excessive salivation or just drooling. But if your dog pants excessively, or drools a lot, then it may reflect an anxiety condition. Other symptoms that this condition can be marked by include white gums, increased rate of breathing and excessive chewing or gnawing at the mouth area or muzzle.
- Reduced appetite or refusing to eat: Anxiety may lead to a loss of appetite or, at best, less food intake than they were “used to.” Not treated promptly, this can lead to weight loss and other health problems.
- Licking or biting themselves excessively: Dogs that are anxious will excessively lick, bite, or scratch their tails or legs. This may lead to skin reaction or soreness, and extra stress or anxiety.
Avoidance or Escape Behavior
Dogs struggling with anxiety often seek to avoid or escape something that they find unpleasant. Common avoidance or escape behaviors include:
- Hiding under furniture or in secluded areas: Some dogs will stay out of sight in the case of a situation that worries them. Some may even choose to sit under a table or a chair and some may prefer to climb into a tiny, confined, and dark area.
- Attempting to escape through doors or windows: Dogs may be afraid of certain things that you say, and their response may be to bark like you are in danger. This can be potentially deadly for the dog and the people must be treated by a vet.
- Refusing to engage with people or other animals: A dog which suffers from anxiety may sever contact with people or other animals or try to escape from them. It worsens stress and loneliness and causes conflict in relationships with people and other animals nearby.
Changes in Body Language
Anxiety in dogs is shown by typical behaviors that mean your dog is uncomfortable. It is necessary to keep heed to a dog’s body language to recognize its anxiety and to find support. Some common changes in body language associated with dog anxiety include:
- Tail tucked between the legs: When a dog is scared or wary, especially of the situation around him, it will lay its tail down and close to its legs.
- Ears pinned back: Sometimes you can see that ears of a dog are pulled back or are pressed to the head it means that the animal is afraid. Such a change of position may be followed by other signs of discomfort, such as whimpering or shaking.
- Avoiding eye contact or lowering their head: If a dog feels threatened or intimidated it may erect its hair or tail or raise its hackles. This behavior is a way of pleading and avoiding an altercation.
Treatments for Dog Anxiety
Managing dog anxiety is not only in changing its environment but also changing some of its behavior as well. Some effective treatments for dog anxiety include:
Introduction to Behavior Modification
Positive conditioning is one of the ways you can use to manage the anxiety affecting your dog in a given situation, as well as using counter conditioning methods of making the dog less anxious in a particular place.
Medication
Sometimes, it may prove necessary to prescribe the dog some medicine to combat his or her anxiety. Anti-anxiety medications effective for dogs include fluoxetine or alprazolam, which will help lower anxiety and enhance the dog’s behavior.
Weight Lifting and Brain Exercise
A dog also needs daily play, as well as physical activities that will reduce stress levels in a dog by exercising and mental stimulation.
Environmental Changes
This article notes that changes in a dog’s environment may be affected with the intent of minimizing anxiety and boosting its securitization. For instance, an opportunity to have refuge or a chance to establish a quiet, and cozy area where the dog can take a rest should be executed.
Training and Socialization
Dog socialization and early puppy training are important because they help the establishment of self-confident behavior patterns with different events. The professionals use various aspect of anxiety related problems and can assist in training techniques.
Conclusion
Dog anxiety is a learned trait that affects so many pet owners and their dogs in today’s society. By reading about the causes and manifestations of the problem, as well as all available methods for its treatment, the owner will be able to start working on the dog’s anxiety and improve the quality of the relationship between the two of them. So, all is not lost with dogs that are anxious and have poor social skills or fear-induced reactions; with a lot of effort, the right attitude and the correct tactics, the canine can be helped to overcome his anxiety and be normal once more.
FAQs About Dog Anxiety
Can all dog breeds experience anxiety?
Yep, it is possible, though some varieties of dog may be predisposed to it and not others. Some of the most sensitive breeds include German Shepherds, Border Collies, and Labrador Retrievers and any of such breeds can be susceptible to anxiety.
How can I tell if my dog is anxious or just bored?
In addition to destruction and other unnatural behaviors, an anxious dog has points such as tremulations, increase in rate of breathing or even tend to seclude itself. While a dog that is anxious will pace and run around in circles, a dog that is bored will just destroy things to keep busy.
Is anxiety more common in older dogs?
However, anxiety can develop at any age, and senior dogs might be anxious because of deteriorating brain function and changes in the senses, and diseases.
Are there specific toys or products for anxious dogs?
Yes, calming toys, puzzle feeders, and weighted blankets are designed to comfort anxious dogs. Additionally, pheromone diffusers can create a soothing environment.
Can anxiety in dogs lead to health problems?
Long term anxiety can cause changes in a dog’s overall health as it affects its immune system further affects the dog’s digestive system and worsens his health complications. This simply means that prompt action must be taken.
How long does it take to treat dog anxiety?
The duration depends on the severity and cause of anxiety. With consistent training and care, most dogs show improvement within weeks to months.