Introduction to Flavonoids
There are many chemical substances in the complex universe of nutritional science that are equally important in maintaining one’s health. Among these, flavonoids are recognized as strong bioactive compounds that can be present in almost any plant food product. But what exactly are flavonoids, why should be concerned?
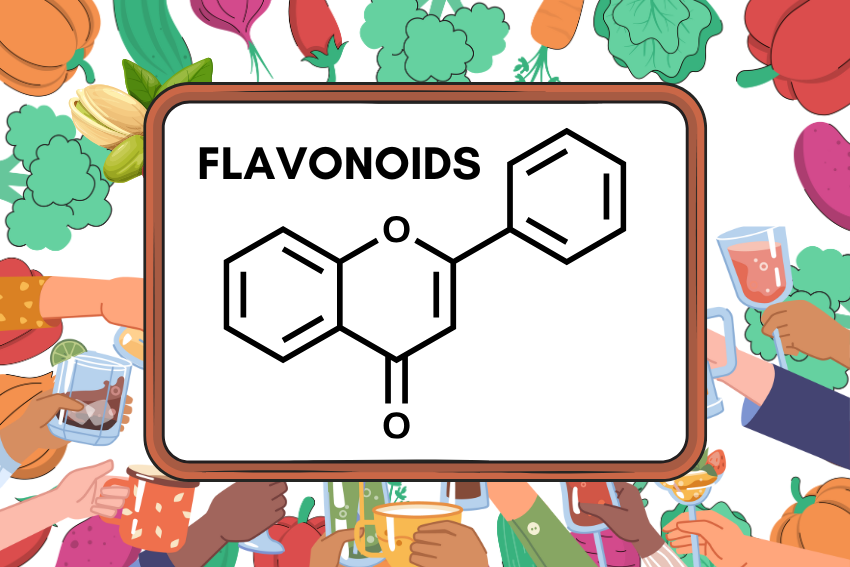
Flavonoids are water-soluble pigments found in almost all higher plants, especially in flowers, fruits, and some vegetables. Despite their primary role in the structure and color of plants, few things are as valuable to man and his dietary needs. They are remarkable molecules that can protect plant cells from the potentially harmful effects of many factors, such as too much sunlight, and can also protect human cells from the havoc of free radicals.
They are also anti-inflammatory and are considered anti-cancer. This makes the position of flavonoids in nutrition and health a vital segment in the strategy to achieve better health standards.
What are Flavonoids?
Flavonoids are bioactive simple organic compounds that occur naturally in fruits vegetables and exclusive plant products. They are part of a larger category of molecules called polyphenols and are characterized by their multiple biochemical and therapeutic functions. Flavonoids are compounds which have the capability to color the human diet due to the presence of plants in which they occur and they contribute to the bright coloration of fruits and vegetables.
Flavonoids are classified into six major classes grouped in sub-families.
- Flavonols (e.g., quercetin, kaempferol): Found in onions, kale, and broccoli.
- Flavones (e.g., apigenin, luteolin): Common in parsley and celery.
- Isoflavones (e.g., genistein, daidzein): Abundant in soy products.
- Flavanones (e.g., hesperidin, naringenin): Present in citrus fruits.
- Flavanols (e.g., catechins, epicatechin): Present in tea, cocoa, and berries.
- Anthocyanins (e.g., cyanidin, malvidin): Responsible for the vibrant colors in berries, grapes, and red cabbage.
Due to their antioxidant properties flavonoids are known to have properties in activities such as decreasing inflammation, boosting the heart health, brain functions as well as stabilizing blood sugar levels. They function through elimination of free radicals from the body and thus slow or prevent the formation of chronic diseases.
Flavonoids also appeared to have cancer preventive effects based on some research and established knowledge so further research is being made in this directions. Some of the effects of the flavonoids are yet to be studied in detail, but including flavonoid-rich foods in your diet is an easy way to promote health. Foods high in flavonoids include berries and apples, citrus fruits and red grapes and wine, tea and dark chocolate.
How do Flavonoids Work in the Body?
Flavonoids are known as antioxidant compounds and may help protect cells from damage that comes with the presence of free radicals. Molecules that are unstable and damage cells and contribute to chronic diseases (like heart disease, cancer, even diabetes among others). As a result of the anti-radical properties of flavonoids, the development of these conditions may be minimized.
However, flavonoids also have an anti-inflammatory effect and since inflammation is the root of some diseases, it is very important. Inflammation is the body’s immune response to injury or infection and while it is a healthy process, if the inflammation becomes long-term it can lead to heart disease, arthritis, and even cancer. Interestingly, flavonoids prevent or treat these diseases by suppressing the formation of pro-inflammatory substances.
In addition, it has also been proved that flavonoids could enhance brain blood circulation and help to enhance the abilities of memory and diminish the possibilities chances of having the Alzeihmers and Parkisons disease.
Health Benefits of Flavonoids
Antioxidant Properties
Flavonoids compounds have shown high antioxidant activities that generally reduce oxidative stress as well as inflammation. They work by eliminating and preventing cell damage by free radicals’ agents that cause oxidative damage. Because of this property, flavonoids are essential for human health to reach the best conditions possible.
Cardiovascular Health
Several works have proved that the intake of foods with flavonoids decreases the chances of developing cardiovascular diseases. Flavonoids have effects on the blood circulation, blood pressure, and anti-coagulative effects. They can also help maintain the right blood lipid profile, making your heart to work as expected.
Improved Brain Function
It has been established that flavonoids have a positive influence on elements of cognitive response such as memory and learning. They can possibly ameliorate age-related cognitive malfunction, offer protection against such diseases as Alzheimer’s, and reduce their severity. This beneficial effect is partly due to the enrichment of flavonoids in the neurons that help to growth new neurons, improve memory as well as reducing inflammation.
Reduced Risk of Cancer
Research conducted to date indicates that flavonoids have anticancer potential since they may act as anticancer agents and supplements. This may be helpful to treat cancer, because they cannot only inhibit the development and growth of cancer cells, but also cause programmed cell death, or boost the immunity of the body. Flavonoids, quercetin and kaempferol have been found to have a potential to lower different forms of cancer.
Improved Digestive Health
Suggested benefits of flavonoid compounds include promoting the growth of good gut bacterium and decreasing inflammation of the digestive tract. Furthermore, they are able to relieve inflammation and pain caused by inflammatory bowel disease, including colitis and other kinds of bowel disorders.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Flavonoids possess an ability to reduce inflammation related diseases like arthritis, asthma, diabetes and lots of fluid build-up which is considerably beneficial. It might block some pro-inflammatory molecules and perhaps change functions of the immune system.
Bone Health
In addition to maintaining the bone strength in body in the flavonoids also have an important role in overall bone health responsible for the modulation of bone formation. They may stimulate proliferation of osteoblasts- bone forming cells- and inhibit osteoclast functioning –bone resorbing cells. This could prevent the spread of future osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
Skin Health
It is worth explaining how and to what extent flavonoids can enhance skin health and opposition to such detrimental factors: inflammation, free radicals, and impaired barrier function of the skin. They can also be useful in slowing down the aging process as they enhance skin’s flexibility, decrease wrinkling and support skin healing.
Dietary Sources of Flavonoids
Flavonoids-containing foods are also grouped into several classes namely fruits, vegetables, beverages, nuts Legumes. The following are some of the most abundant dietary sources of flavonoids:
Fruits
Fruits contain flavonoids, such as anthocyanin and flavanols. They are blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, strawberries and elderberries, which are known to contain flavonoids. Other fruits include cherries, grapes, apples, and pears too contain this mineral in plenty. Oranges contain flavanones while Kiwifruit contains kaempferol.
Vegetables
These include but are not limited to broccoli, kale, spinach, most of the green leafy vegetables and so on which have flavanols such as quercetin, kaempferol, and isorhamnetin. Flavonoids are also found in onions, bell peppers as well as tomatoes. Intake of more of these colorful vegetables is well encouraged to improve the flavonoid consumption in its consumers.
Beverages
Tea, red wine and cocoa are examples of flavonoid containing foods and beverages. Both green and white tea contain a good percentage of catechins and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). Red wine contains the flavonoid chemicals that is quercetin, kaempferol, Myricetin with resveratrol. Flavanols found in cocoa are the flavanols such as epicatechin and catechin.
Nuts and legumes
Almonds, peanuts, soybean and nuts and legumes contain flavonoids such as quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin. Moreover, necessary flavonoids also may be obtained from dark chocolates since they are produced from cocoa beans.
Spices and herbs
The flavonoids present in most spices and herbs are usually high. Thyme, sage, rosemary, and turmeric contain examples like for instance, Rosmarinus acid or quercetin, kaempferol and curcumin.
Flavonoids and Gut Health
Flavonoids can be described as a category of naturally occurring compounds that exist in many plant-based foods that include fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grain as well as other plant derived edible products. These compounds exhibit strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects, and are associated with multiple benefits to human health.
It is widely understood that flavonoids have an essential function in gut health. It is a term for the human gut microbial flora made up of bacteria, fungus, viruses. And these are all involved with how your system works properly, they work for the digestive system, metabolism, and the immune system, and so on.
Research has illustrated that flavonoids can subdivide the beneficial effects on the growth of bifidogenic bacteria in the gut and the suppression of pathogenic bacteria. For example – flavonoids help increase the production of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced by bacteria in the gut. SCFAs are useful for the repair of damaged gut lining and have anti-inflammatory properties.
Also, flavonoids have been found to have prebiotic characteristics, which helps stimulate the activity of the beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract without being used up by the bacteria in the upper part of the gastro-intestinal tract or being absorbed. That’s important because the gut microbiota is one of the major players in colon health.
Finally, flavonoids essentially play role in regulating bacteria growth which is beneficial to gut as well as suppression of the bad bacteria and stimulation of the synthesis of SCFAs. Beneficial gut bacteria can hold flavonoids which in turn are useful for meeting our every need as humans hence the importance of the foods containing flavonoids.
How to Optimize Flavonoid Absorption
Flavonoids are a class of naturally occurring compounds found in plants and have been found to have several positive effects to health. To optimize flavonoid absorption, consider the following tips:
Consume a wide variety of flavonoid-rich foods
More flavonoids should be obtained through the consumption of different products like fruits vegetables and kernels and pulses and nuts and seeds. This will make it easier for you to be able to receive different sorts of flavonoids and thus all the health gains associated with them.
Pair flavonoid-rich foods with fat
It has been found that flavonoid-rich foods when taken with some sort of fat enhance the bioavailability of flavonoids. For instance, when you are having berries the defaults consist of a serving of berries with nuts, and when having flavonoid rich vegetables, a source of of healthy fat such as avocado or olive oil should be added to the salad.
Cook with flavonoid-rich ingredients
This can be done by using ingredients rich in flavonoids in preparation of your food for instance using cocoa powder or turmeric.
Avoid consuming flavonoids with high-antioxidant foods
Some high-antioxidant foods such as pomegranate juice or blueberry juice can also reduce the ability of the body to absorb flavonoids. To get the best benefits of flavonoids in these types of beverages, make sure that you don’t consume them with other flavonoid-containing food products.
Consider supplements
However, if you’re unable to consume flavonoid-rich foods in adequate quantities every day, you might opt for flavonoid supplement. However, the author should recommend that a doctor be consulted before commencing on any new supplementation.
Are There Risks or Side Effects?
There are of course unwanted effects or complications that can come with different treatments, drugs, or changes in behavior, and these should be known before any action is taken. The side effects vary from mild and transient, moderate and long lasting to severe side effects of the drugs.. So, for example, a drug for a given disease might have side effects like dizziness and stomach problems in certain people.
Furthermore, some medical procedures that are performed come with the risk of getting an infection, developing blood clots or bleeding, or having an allergic reactions to anesthesia. When it comes to any medical treatment it is very important to find out whether the pros of the treatment are greater than the cons including the side effects of the drug. To make the best decisions for your health care it is always effective to consult your healthcare practitioners.
In addition, taking up new behaviors of exercising, smoking cessation, altering your diet also has potential bumps and strain. Although, with requisite tenacity and encouragement, the barriers can be surmounted and most people attain their health objectives.
Do everything the doctors tell you to follow and do as extensive research as possible into any treatments, drugs or changes of behavior. It can also help you gain a clearer perspective of what the risks are, side effects and possible benefits providing the patient which a better empowered approach to the management of their health.
Conclusion
Flavonoids may be classified as naturally occurring bioactive compounds found in many fruits, vegetables, and other plant produce, in a manner of speaking. Also known as these antioxidants and anti-inflammatory, are crucial in keeping a body and mind strong and healthy.
Eating meals with flavonoid-rich foods in many of these cases benefits the heart, the mind, and could even lower the danger of contracting various diseases. Also, one must keep in mind that the facts about the positive health effects of the flavonoids are even doubled when taken together along with proper balanced diet and exercise regimes.
Therefore, it is advisable that you take many foods that have flavonoids that are easily available such as berries, citrus fruits, apples and green tea among others to benefit from these compounds.