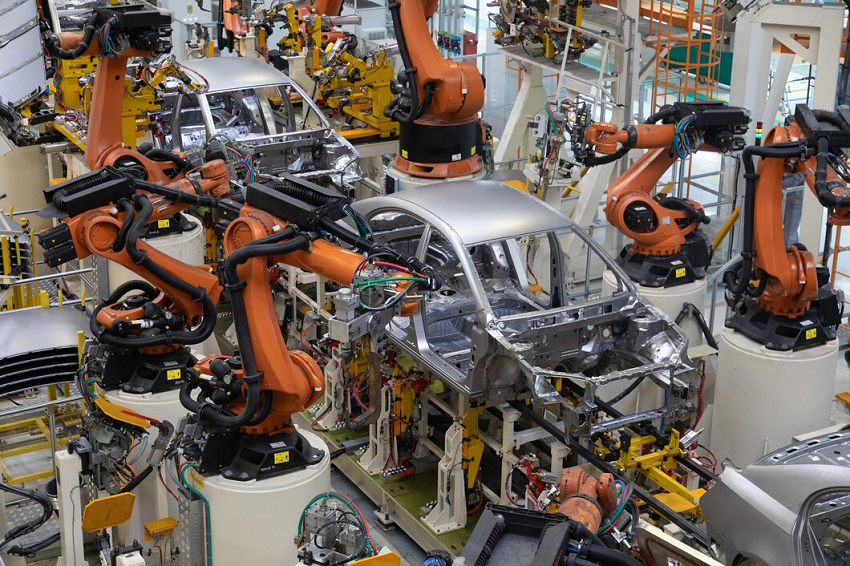
Introduction to Robots in Automotive
Growth in the automotive industry has been a dynamic process over the century that changes from manual made automobiles to fully automated assembly lines. Because of globalization and with the mechanization of the production line, manufacturing firms have had to adopt robotics in a bid to improve efficiency, quality, and costs. The integration of robots in automotive assembly is not only the case of the use of new technology but a different model of constructing automobiles. This article discusses the diagrammatic advantages of the use of robotics in the automobile industry, popular uses, the new developments, issues, and the outlook in the industry.

Benefits of Robotics in Automotive Assembly
Robotics has benefited automotive manufacturing in a number of ways, thus enhancing it through innovation. Here are some of the key benefits the integration of robots in automotive assembly.
1. Increased Efficiency
Perhaps the biggest added advantage of the robotic integration in assembly is the improvement of efficiency by a huge margin. People get tired in the course of duty but robots independently can work on a round the clock basis to meet the required production schedule. This capability enables the manufacturers to cut the cycle times down by a large percentage and an overall increase in production rates. For example, while a human worker will need to rest, a robot, for example, used for welding or painting exercises can go on for hours without the need to stop.
Also, robots are able to work and execute tasks with high accuracy and speed in comparison with human beings. This efficiency leads to shorter cycles of production, it’s easier for the companies to meet the market needs and cut down lead times. Within such a competitive market, one key factor that would work towards the benefit of a company is a faster way of assembling vehicles.
2. Improved Quality
Creating quality products is very important in the automotive industry because nothing is as sensitive as a car that must be full of safety features and guarantee to produce good results without failing. Integration of robots in assembly processes benefits the quality of the assembly processes as it guarantees accuracy and uniformity. For instance, robotic welding systems are programmed with options for sensing and control capabilities to make corrections thus providing stronger and reliable welded joints.
Further, robotic painting systems use advanced techniques that allow coverage of the targeted surface uniformly with reduction of defects. Robots do not tire or get easily distracted which make them produce fewer mistakes when painting the car as compared to human beings. This consistency not only enhances the general quality of the vehicles that are being produced but also eliminates tendencies of having to recall or repair some of the vehicles at extremely high costs.
3. Cost Reduction
The drawback of acquiring robotic systems is that they may be very expensive initially but in the long run, it is very economical. Automation of repetitive activities helps to eliminate labor costs as well as assignments workers to the higher tasks that need problem-solving skills. This shift enables organizations to deploy the limited human resources most effectively and efficiently and at the same time reduces the costs of labor.
In addition, robotics help to achieve material savings, since the rate of losses during product production is significantly reduced. For instance, manufacturing execution includes fine quarries in robot cutting and welding that eliminate unnecessary material, which may prove costly and environmentally damaging. The combined impact of such cost savings can help deliver better operating margins as companies have extra cash to invest in innovation with a view to improving their footprint.
4. Safety Enhancements
Safety has become a priority more especially for companies within the automotive manufacturing industries. This is because robots can easily be employed in areas which are considered to be dangerous and this will reduce the incidents of accidents. For example, robots are able to lift heavy parts, carry out dangerous welding operations as well as work with hazardous chemicals. Thus, it is possible to state that robots’ completion of such risky tasks can contribute to the reduction of employees’ risks within the framework of their work.
Further, incorporating of collaborative robots or cobots has also increased safety in the assembly in automotive industry line. Cobots are not intended as a replacement for the human operator but rather a companion that assists in operation. These robots are fitted with sensors and other sophisticated systems to enable them to identify human beings and change their actions. By these means, it also becomes possible to guarantee an appropriate safety of the working process environment.
Common Applications of Robots in Automotive Manufacturing

In this segment, the various uses of robots in automotive manufacturing are enumerated as follows; Here are some of the most common applications:
1. Robotic Welding
Robotic welding is one of the most commonly adopted areas in the automobiles manufacturing process. Numerous industrial robots, for example robotic arc welding equipment are used in spot welding and laser welding. This welding makes it possible for the vehicle manufacturing industries to automate welding hence increasing on the strength in the manufacturing process.
For instance, automotive industries employ robotic welding systems in order to join chassis part to other part. These robots are compact and can excrete specific amounts of pressure and thus can produce a weld that is safe and reliable. Consequently, it becomes possible to design vehicles which look beautiful and are strong and safe at the same time.
2. Robotic Painting
Another area where robotics have proved very useful is in painting, which is another important application. Automated painting systems apply recent spray technology in painting without leaving seams on the body of the car. Some of these systems are capable of controlling the application of paint patterns and angles and this can be done in real-time.
Thus, the advantages of robotic painting can be many more than just the artistic consideration. Another advantage of this automated painting system is that most of the time, the human operators, painters, etc. must work with very dangerous substances; with such an automatic painting system, the manufacturers would reduce the chances of human operators coming into contact with dangerous substances. Also, robots can work in a clean environment that would minimize contamination and guarantee a well-done job.
3. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots, or in other words, collaborative robots have become a new generation of robots dominating automotive assembly. Cobots are aimed at helping the human operators in performing their tasks of the operations with high efficiency without evicted human operator’s job. For example, a cobot can help a worker by fitting heavy components or performing repetitive operations.
This is because cobots are flexible and can easily integrate with a changing manufacturing system as it adapts to new needs. They can be easily programmed for different tasks and can also be reconfigured for other uses to accommodate other product lines thus making them an important tool for car manufacturers who are looking to become more flexible in their operation.
4. Material Handling
Transportation of materials within assembling facilities is important in automotive manufacturing, and robots provide efficiency for design in material handling. AGVs are mobile robotic systems that are used to prevent the flow of material, components and finished vehicles in the production process throughout the manufacturing plant.
AGVs are self-propelled, thus, the vehicles can be pre-programmed to move along any desired route or to use sophisticated instrumentation to detect the presence of other vehicles of objects in the immediate operating environment. This automation helps curb the use of muscle power in moving items from one location to another, so that people can use their muscles to do other work which is more valuable. In the same way, AGVs also increase throughput since it eliminates delays in transporting goods to the right place at the right time.
Trends in Robotics Integration
The integration of robots in automotive assembly is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Here are some key trends shaping the future of robotics in the automotive industry:
1. Shift Towards Final Assembly Automation
The last assembly has been identified over the years as one of the most intensive in terms of work and time in car production. Still, with regards to these, manufacturers are slowly implementing them with the use of collaborative robots and complex automations. This shift is beneficial as it makes the assembly of vehicles more efficient and not to mention much less reliant on manual labor.
For instance, current applications of robotic systems include mounting of dials, fitting of doors and even complex parts. It has been found that this trend helps increase productivity while at the same time increasing the quality of the assembled vehicle.
2. Adoption of Advanced Technologies
Current trends in the automotive context raise questions on the fusion of sophisticated technologies including vision, artificial intelligence, and internet of things in robotic systems. They help the robots to make decisions within a given process flow and within due feedback received from the available sensors and cameras in a production to enhance productivity and quality check.
For instance, in machine vision applications the defects in the components/assembly can be easily identified by robots and they can make the necessary corrections on the assembly line. AI also has the capability to read production data and determine any areas that must be addressed to increase the efficiency of the operation. These technologies are advancing in unison and are set to define further automation of the automobile assembly line.
3. Flexibility and Customization
Cars have become more specialized to meet consumers’ changing tastes, while placing pressure on the manufacturers. This demand for customization has resulted in the request for versatile robotic systems suitable for change in product types and arrangements. Some contemporary robots are flexible in case of programming and redesign, so several models can be produced on the same line.
This flexibility is important in order to deal with the increasing number of orders for EVs and hybrid vehicles which need different assembly than regular ICE vehicles. Hence, some of the manufacturers that are in a position to adapt their production capacities will perform better in the constantly transforming auto industry.
Challenges and Considerations
While the integration of robots in automotive assembly offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that manufacturers must address:
1. Initial Investment Costs
One of the principal disadvantages associated with the use of robotic systems is the capital needed to deploy them, which could be costly to many manufacturers, especially those that are small establishments. Initially, the cost of buying the robots and coding the robots plus the process of modeling the robots in the production could be very expensive. But these manufacturers have to factor in the efficiency that automation is likely to bring in the long run before evaluating these costs.
2. Training and Workforce Adaptation
The integration of robotics within automotive assembly also brings in more demand towards training and workforce adjustment. There is a need to prepare human workers to be able to deal with robots and automated systems. This may entail large costs for training programs and workplace development and learning to guarantee that employees are ready to deal with the current changes in manufacturing.
3. Maintenance and Upkeep
Any robotic system has to be maintained often to reach its maximum capacity and to avoid as many malfunctions as possible. It is imperative that manufacturers put into place proper maintenance plans to deal with the problems should they arise. Moreover, the firms should propose responses for unpredictable failures and guarantee that the timetables for manufacturing are not interrupted.
Future Perspectives
The integration of robots in automotive assembly is expected to grow more in the future, and the aspect of robotics in automobile manufacturing is expected to grow also in the near future. Here are some key perspectives on the future of robotics in the automotive industry:
1. Continued Growth of Automation
The automobile industry is set to experience a high level or Automation in the near future as innovation sets in and organizations embark on the search for efficiency. Forecasts show that the use of robots will gradually increase as the producers aim to increase output and, at the same time, minimize expenses.
2. Innovations on the Horizon
Future developments in robotics technology have several emerging innovations which are expected to take robotic systems in automotive assembly to another level. All these advancements are not only going to make robots work faster but are also going to extend the capability of robots to perform the tasks.
3. Sustainability Considerations
With the growing concern of the automakers industry on their environmental impacts, the use of robotics can be a great asset in creating sustainability in manufacturing. As evident from the arguments above, its incorporation can play a role in bringing change to the overall processes in a more sustainable way.
Conclusion
The integration of robots in automotive assembly has revolutionized the manufacturing process through improving the quality, efficiency, and overall safety. Looking optionally at the near future, we will establish how the development of automation as well as other innovations and sustainability factors, will significantly alter the car manufacturing sector.
This is an implication that manufacturers cannot shy away from integrating robotic systems in order to produce commodities that can compete in the global market. Flexibility in responding to the shifts in consumers’ preferences, the use of innovative solutions and solutions friendly to the environment will be decisive in the future market situation.
Robotics and automation as a substitute for labor thus make manufacturers ready and relevant in an environment that is more efficient than before, sustainable, and even sensitive to consumer needs. Automated and sustainable assembly for the automotive industry is still in its very early stage and the future opportunities are enormous.